THE SCIENCE OF MAGNAWAVING AND THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN LOW AND HIGH INTENSITY PEMF
THE SCIENCE OF MAGNAWAVING
Gather round as we discuss the science of MagnaWaving and the differences between low and high-intensity PEMF. The science of PEMF must be understood before we dive into the differences between high and low intensity. As we go into this discussion it’s important that you know what we know, Dr. Robert Dennis says in a recently published article, “The truth is we know what pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) does but we don’t know how it does what it does.”
WHAT DOES PULSED ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS DO?
PEMF (pulsed electromagnetic field) comes down to maintaining good cell health. The stresses of everyday life from our environment, to sports and work, take a toll on our bodies. As a result, our cells no longer function at their best which leads to premature aging, degenerative diseases, and decline in performance. By stimulating cell metabolism, MagnaWave may restore cell function and help the body repair cells and recover from illness.
PEMF aids the body in a number of ways, such as:
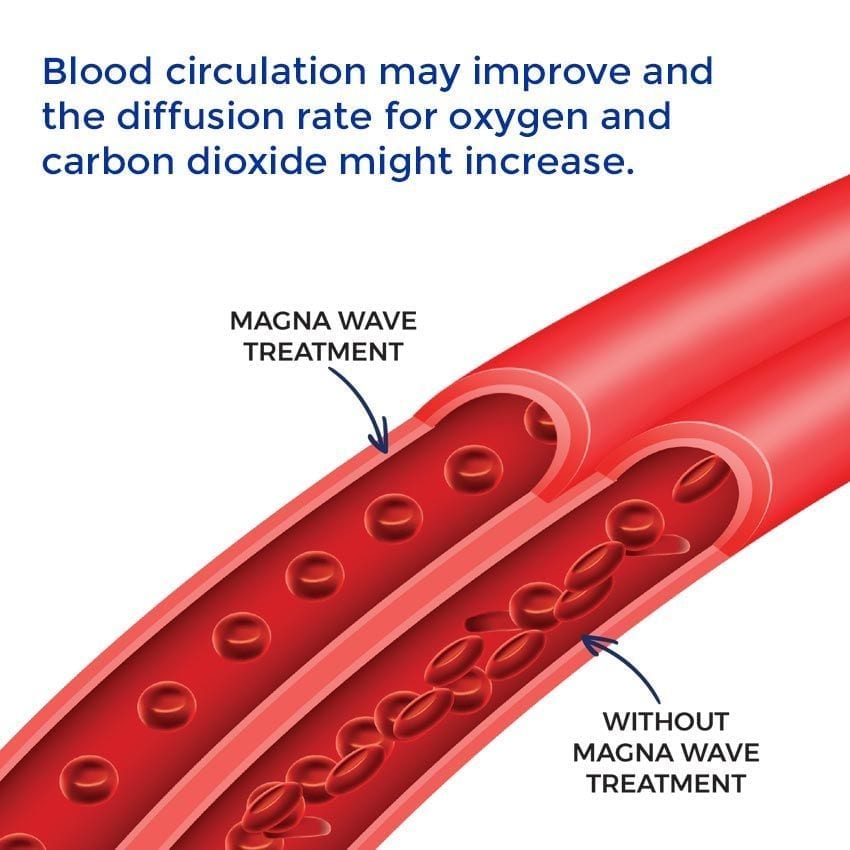
- Blood Circulation: Loaded particles in the bloodstream seem to oscillate in rhythm with the PEMF frequency. This may reduce friction and flow resistance, especially in narrow capillaries. Blood circulation may improve and the diffusion rate for oxygen and carbon dioxide might increase.
- Oxygen Partial Pressure: Many PEMF studies appear to demonstrate an increase in blood oxygen content. Cell membrane potential also seems to become regulated. Exhaustion caused by stress or chronic disease can reduce cell membrane potential (70 to 90 mV). When a cell reaches the zero level, it dies. Cells use 50% of their energy to maintain their optimum potential. MagnaWaving, with its ion transport system may enable the selective movement of protons (H+ ions). H+ ions are then retargeted to the cell membrane, in turn the cell membrane becomes hyperpolarized then normalizes.
- Calcium Influx: Via the potentially increased concentration of H+ ions in the cell membrane, it has been noted that the PH value is said to be reduced near it. This may lead to the release of calcium from the protein layer of the cell membrane. This released calcium might flor into the cell core, triggering multiple metabolic reactions:
- Macrophages: tissue cells functioning as protection against infection may become activated, strengthening the immune system.
- Metabolism: as a byproduct of an activated metabolism, nitric oxide (potentially a vessel enlarger) may be produced.
- Cytogenesis: structure, function and multiplication of the cells is stimulated.

THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN LOW AND HIGH-INTENSITY PEMF
Now that we understand what MagnaWaving does, let’s talk about the differences we observe between high and low-intensity PEMF. First, we want to note that both high and low intensity are beneficial. The most notable difference is in the amount of time it takes to achieve those same benefits. What we don’t know (and one of the reasons we don’t establish protocols) is exactly which combination of intensity and frequency are optimal for the goal you’re trying to achieve. One reason for this is that we are all different and each situation is different. That said, let’s highlight the differences between the two intensities:
LOW-INTENSITY PEMF
- Low-powered intensity (low gauss: in milli-gauss)
- Benefits capillary blood flow skin deep
- Longer sessions
- More frequent sessions are needed
- Great for relaxation and healing
HIGH-INTENSITY PEMF
- High powered intensity (high gauss: in the thousands)
- Immediate results
- Benefits systemic circulation
- Shorter sessions
- Great for relaxation and healing

MagnaWave offers both high and low-intensity equipment, like the MagnaWave Pro (high-intensity) or the MagnaWave EZY coil (low-intensity). Although, we do specialize in high-intensity because we enjoy the faster results.
It really comes down to what you’re trying to achieve, and in what time frame you’re trying to achieve it. Both high and low-intensity are effective and beneficial but it’s up to you to decide which is right for you and your goals.

